Rural areas and remote Villages are often at a disadvantage in terms of access to electricity. The high cost of providing this service in low populated, remote places with difficult terrain and low consumption results in rural electricity schemes that are usually more costly to implement than urban schemes.
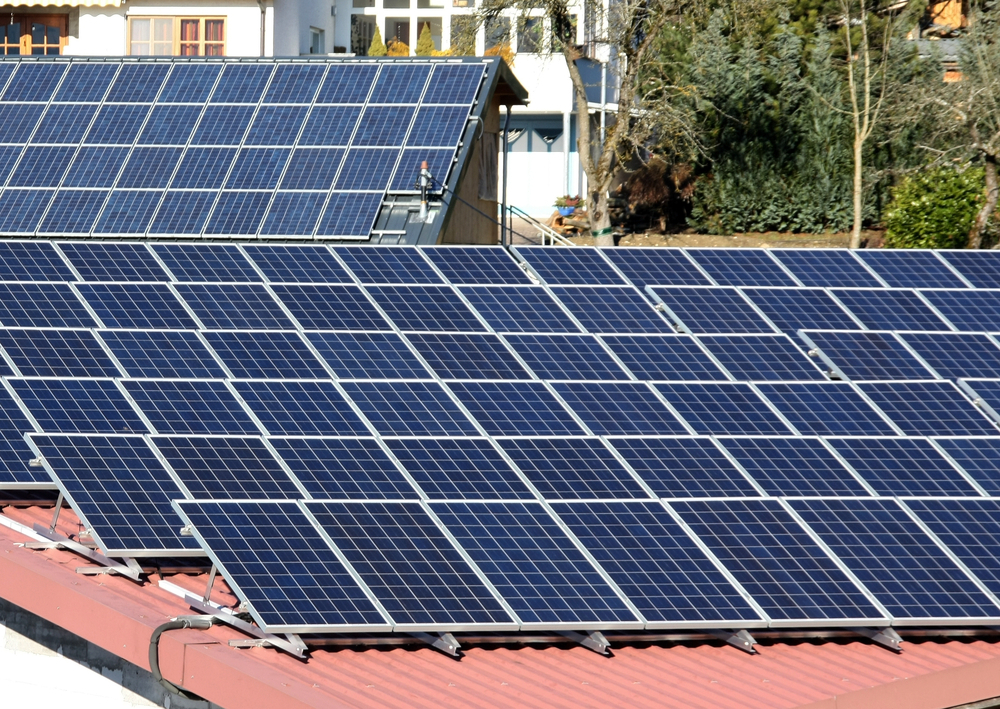
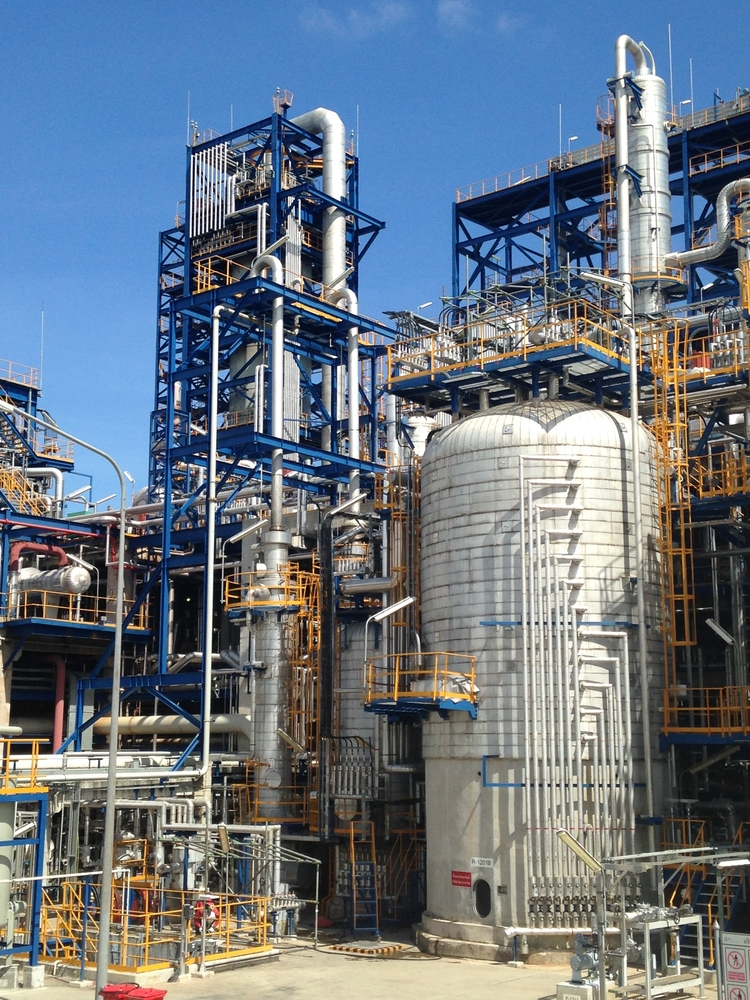
Solar power is the conversion of sunlight into electricity. Concentrated Solar Power (CSP), in which sunlight is focused on an area containing water which is converted into steam and is used to generate power, as in a thermal power plant. CSP produces concentrated solar beam irradiation to heat liquid, solid, or gas as in a regular TPS. The best sites for CSP are in equatorial belt cloud-free regions.
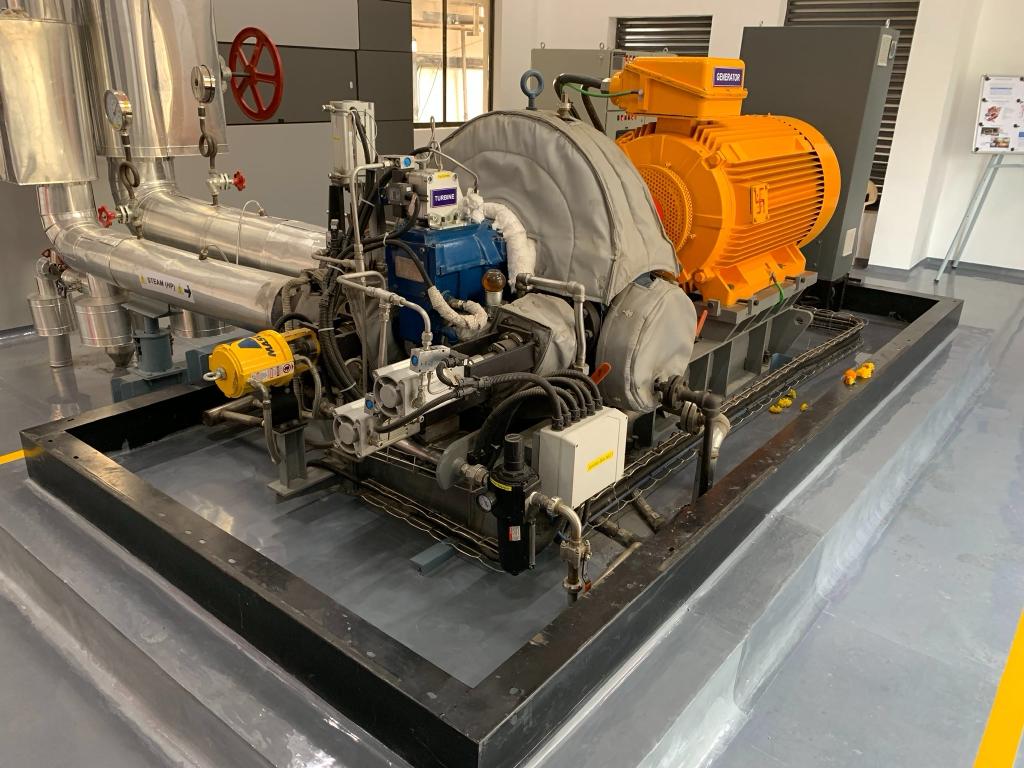
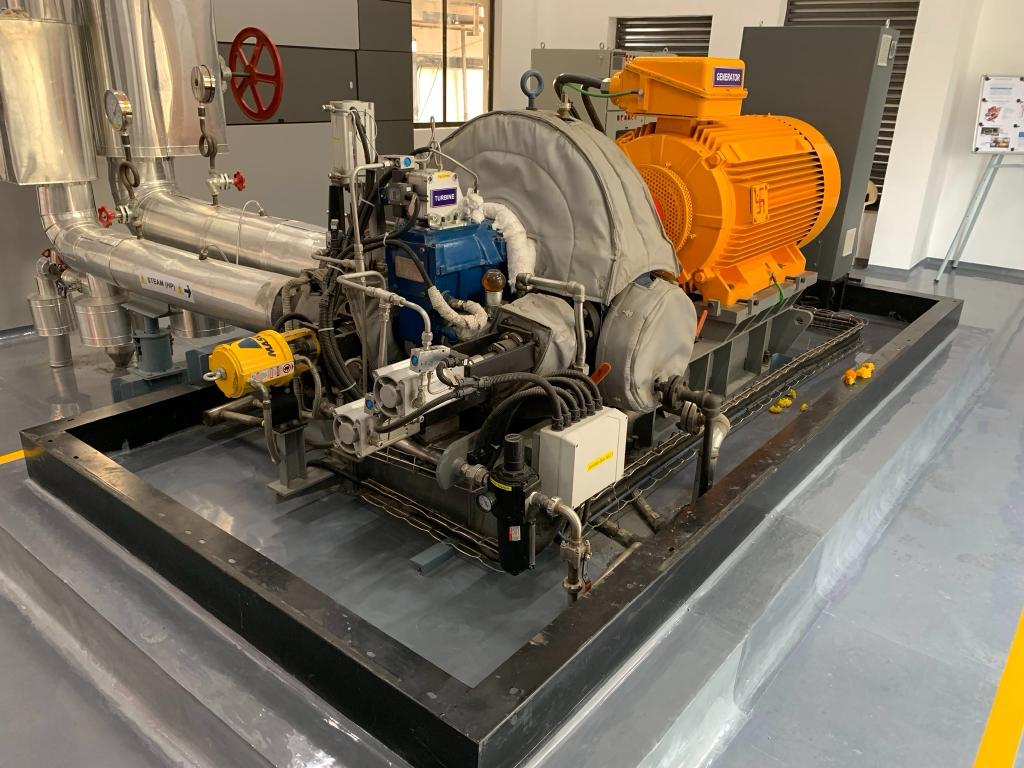
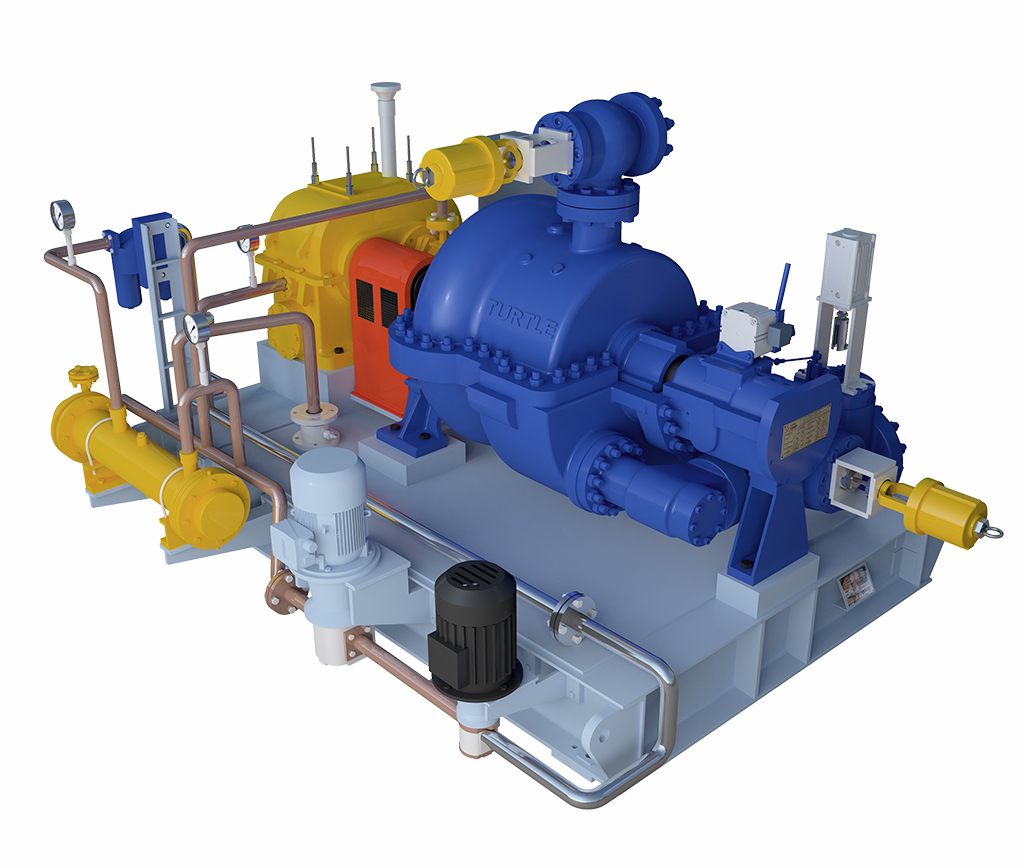
Solar thermal power plants use the sun’s rays to heat a fluid to high temperatures. The fluid is then circulated through pipes so that it can transfer its heat to water and produce steam. The steam is converted into mechanical energy in a Steam Turbine which is then converted into electricity by a conventional generator.
Thus providing power to remote villages which can be effectively used for Irrigation, improves the individual quality of life, facilitates community services such as health and education, and enables business entities to carry out professional activities for rural populations.
Turtle Turbines have supplied Steam Turbine to Solar Thermal Plant at Shive in Pune with Thermax. The project was funded by the Government of India.